Description
The aim of Reference Book for Hindu Philosophy is the extinction of sorrow and suffering by the method of knowledge that alone can free man from the bondage of ignorance. It points to a clear way of thinking which enables one to understand Reality by direct experience. From this perspective, Hindu Philosophy is an art of life and not a theory.
In this book, the author presents a precise and illuminating study of six systems of Indian Philosophy classified into three divisions: (1) Nyaya-Vaisesika, (2) Samkhya-Yoga, and (3) Mimamsa-Vedanta. The first division lays down the methodology of science and elaborates on the concepts of Physics and Chemistry to show how manifestations of phenomena come into being. The second division sets forth an account of cosmic evolution on purely logical principles. The third division critically analyses the basic principles; developing them in greater detail and furnishing arguments to substantiate, as well as making incidental contributions on points of special interest.
Besides presenting an account of the Philosophical Systems of india the author adds a study of Kashmir Saivism - a system of Ideal Monism founded by Vasugupta and based on Siva Sutras. In this context, the author throws sufficient light on the traditional Tantric literature that has suffered wide criticism both from Western and Eastern scholars.
The book is documented with a Preface, Introduction, and Glossarial Index.
This book is an attempt to outline the essence of the six classic systems of Hindu Philosophy namely, Nyaya, Vaisesika, Samkhya Yoga Mimamsa, and Vedanta. All other schools of thought are but variations of these six. I felt it necessary to present only one additional school namely Kashmir Saivism which gives the most detailed analysis of the ultimate principle however it can hardly be fully understood until the other six systems are comprehended.
To understand correctly Hindu Philosophy it is paramount that one realize that the basis of all the schools is the same. Together they form a graduated interpretation of the Ultimate reality. Each school is based on the same metaphysical doctrine while discussing some particular aspect of the whole. For example, Nyaya discusses the means by which knowledge may be had of the Ultimate reality Vaisesika the things to be known about that Ultimate reality Samkhya the evolution of Metaphysical doctrine Yoga the metaphysical doctrine in relation to the individual Mimamsa the rules and method of interpreting the doctrine Vedanta the relationship between God Matter and the world and Kasmir Saivism the nature of the Ultimate spirit and the show the interrelationship of these schools and how each assumes the doctrines of the other while it solves its special problem.
In this introduction to the classic Philosophical Schools of india there is no attempt to prove or disprove but rather to present the system of each school many eminent scholars have ably discussed the philosophical implicational in full detail. My problem has been one of deciding what would be omitted rather than what should be included. Only the essentials of each system are presented.
According to the classic schools of Hindu Philosophy, the method by which the individual can evolve himself during this life is through the practice of Yoga. This is the universal technique recommended to enable man to acquire actual insight into the true nature of things. All schools agree that until the faith is fortified with understanding little progress can be made for knowledge without application is like medicine that is not taken.
To aid those who do not have a knowledge of Sanskrit each term in most cases is defined when it is introduced giving the seed concept of the word so that the intended metaphysical idea can be more readily grasped. For future reference a glossary of all important term has been provided in the hope that it may aid those who wish to read some of the recommended bibliographical material. In the use of the English translation of these technical Sanskrit terms one is cautioned not to take them literally for it is impossible to adequately translate them. Various writers have used different translations which will be source of confusion at first. However if one learns to use the technical term he will son grasp its full connotation.
This work is a systhesis rather than an original contribution. In its preparation, I have relied extensively upon the writings of recognized authorities on Hindu philosophy. For the sake of Simplification I have avoided extensive use of quotations and footnotes and I have made use of the traditional chronology throughout without comment.
In conclusion I wish to express my gratitude to those authors listed in the bibliography from whose works I have drawn special mention should be made of two outstanding guides Indian philosophy by S. Radhakrishnan and A History of Indian Philosophy by S. Dasgupta I am also indebted to Prof. Herbett W. Schneider for many helpful recommendation in the preparation of the manuscript and to Prof. Louis H. Grey for his constructive criticism and technical assistance.
| Preface | vii |
| Introduction | 1 |
| Purpose of Hindu Philosophy | 2 |
| Test of Philosophy | 3 |
| The Darsanas | 4 |
| Influence | 7 |
| Samkara | 7 |
| Ramanuja | 9 |
| Madhva | 11 |
| Kasmir Saivism | 12 |
| The Tantras | 13 |
| Saivism | 17 |
| Saktism | 18 |
| Vaisnavism | 18 |
| Nyaya | 20 |
| Purpose | 21 |
| Scope | 22 |
| Philosophy | 23 |
| Literature | 41 |
| Vaisesika | 43 |
| Purpose | 44 |
| Scope | 45 |
| Philosophy | 47 |
| Paramanus | 47 |
| Akasa | 54 |
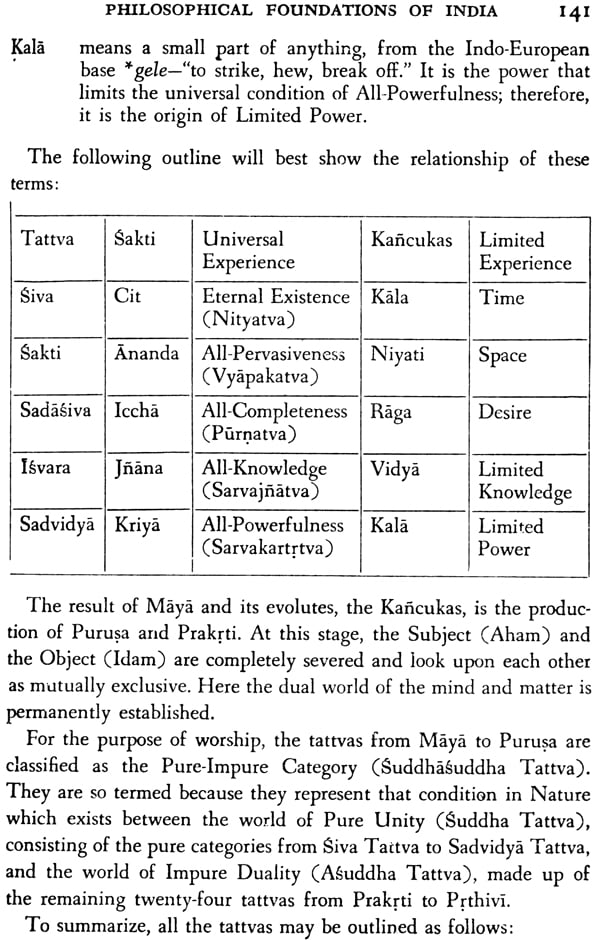
| Kala | 56 |
| Dik | 57 |
| Atman | 58 |
| Manas | 62 |
| Literature | 64 |
| Samkhya | 66 |
| Purpose | 67 |
| Scope | 67 |
| Philosophy | 69 |
| Purusa | 70 |
| Prakrit | 72 |
| The Ganas | 74 |
| Mohat | 77 |
| Ahmkara | 77 |
| Manas | 78 |
| Indriyas | 78 |
| Tanmatras | 79 |
| Mahabhutas | 80 |
| Literature | 82 |
| Yoga | 86 |
| Purpose | 87 |
| Scope | 88 |
| Philosophy | 89 |
| Jiva | 91 |
| Gunas | 92 |
| Citta | 94 |
| Buddhi | 95 |
| Ahamkara | 95 |
| Manas | 96 |
| Indriyas | 97 |
| Tanmatras | 98 |
| Bhutas | 99 |
| Literature | 100 |
| Mimamsa | 101 |
| Purpose | 102 |
| Scope | 102 |
| Philosophy | 103 |
| Literature | 112 |
| Vedanta | 116 |
| Purpose | 116 |
| Scope | 117 |
| Philosophy | 120 |
| Brahman | 123 |
| Atman | 125 |
| Maya | 126 |
| Literature | 127 |
| Kashmir Saivism | 129 |
| Purpose | 129 |
| Scope | 130 |
| Philosophy | 133 |
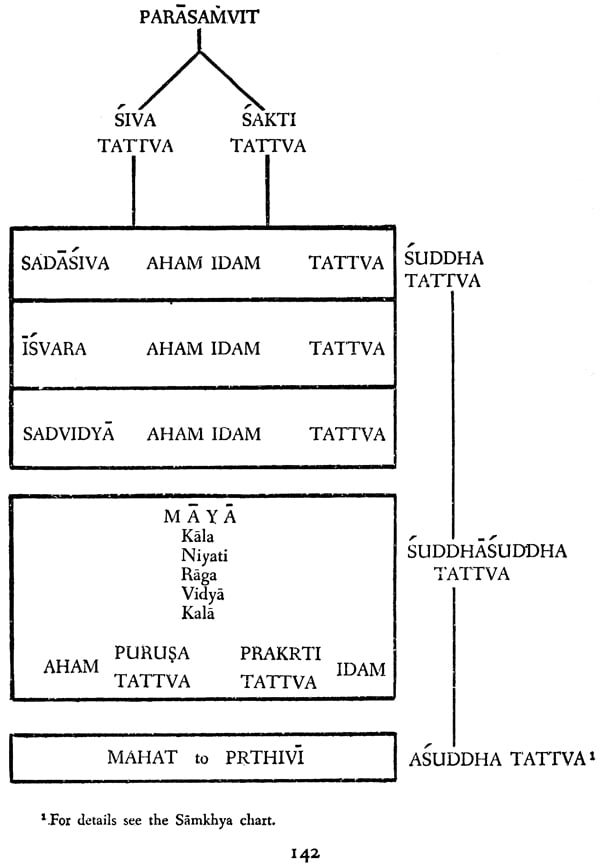
| The Siva Tattva | 135 |
| The Sakti Tattva | 136 |
| The Sadasiva Tattva | 137 |
| The Isvara Tattva | 138 |
| The Sadvidya Tattva | 138 |
| The maya Tattva and its evolutes | 139 |
| The Kancukas | 140 |
| Literature | 143 |
| General works | 146 |
| Nyaya | 148 |
| Vaisesika | 150 |
| Samkhya | 151 |
| Yoga | 152 |
| Mimamsa | 153 |
| Vedanta | 154 |
| Kashmir Sivaism | 156 |
| Abbreviations and Symbols | 156 |
| Glossary | 157 |
| Index | 208 |